Mac Connected To Wifi But No Internet Library
- Mac Connected To Wifi But No Internet Library In The World
- Connected To Internet But No Access
- Mac Connected But No Internet
- Imac Connected To Wifi But No Internet
If you've followed the steps to connect your Mac to a Wi-Fi network, but the connection to your network or the Internet isn't reliable, the steps in this article might help.
Since I own a OnePlus 6 I always have the problem that Spotify is offline when I connect to a WiFi. When I disconnect from WiFi and use mobile internet Spotify works fine. When I reinstall the app spotify works via WiFi until I leave the WiFi. After that I experience the same behavior as before. Feb 15, 2014 Suddenly I now can't access the internet EVEN though my computer is still connected to the router. The WiFi is green and says the name of the WIFI connection but I get nothing. My phone and old white macbook (that i'm using now) still works with the wifi but not my macbook pro. I have no idea how to go about solving this issue, any help?
Check for Wi-Fi recommendations
When your Mac tries to connect to a Wi-Fi network, it checks for issues that affect its ability to create a fast, stable, and secure connection. If an issue is detected, the Wi-Fi status menu in the menu bar shows a new item: Wi-Fi Recommendations. Choose it to see recommended solutions.
Wi-Fi recommendations are available in macOS Sierra or later.
Analyze your wireless environment
Your Mac can use Wireless Diagnostics to perform additional analysis.
- Quit any apps that are open, and connect to your Wi-Fi network, if possible.
- Press and hold Option (Alt) ⌥ key, then choose Open Wireless Diagnostics from the Wi-Fi status menu .
- Enter your administrator name and password when prompted.
Wireless Diagnostics begins analyzing your wireless environment:
If the issue is intermittent, you can choose to monitor your Wi-Fi connection:
When you're ready to see recommendations, continue to the summary. Wireless Diagnostics asks for optional information about your base station or other router, so that it can include that in the report it saves to your Mac.
Click the info button next to each item in the summary to see details about that item. Wi-Fi best practices are tips that apply to most Wi-Fi networks.
Mac Connected To Wifi But No Internet Library In The World
Back up or make note of your network or router settings before changing them based on these recommendations—in case you need to use those settings again.
Monitor your Wi-Fi connection
Your Mac can monitor your Wi-Fi connection for intermittent issues, such as dropped connections. Follow the steps to analyze your wireless environment, but choose ”Monitor my Wi-Fi connection” when prompted.
During monitoring, a window shows that monitoring is in progress. Monitoring continues as long as this window is open and you're on the same Wi-Fi network, even when your Mac is asleep.
If Wireless Diagnostics finds an issue, it stops monitoring and shows a brief description of the issue. You can then resume monitoring or continue to the summary for details and recommendations.
Connected To Internet But No Access
Create a diagnostics report
Wireless Diagnostics automatically saves a diagnostics report before it displays its summary. You can create the same report at any time: press and hold the Option key, then choose Create Diagnostics Report from the Wi-Fi status menu . It can take your Mac several minutes to create the report.
- macOS Sierra and later saves the report to the /var/tmp folder of your startup drive, then opens that folder for you.
To open the folder manually, choose Go > Go to Folder from the Finder menu bar, then enter /var/tmp. - OS X El Capitan or earlier saves the report to your desktop.
The report is a compressed file with a name that begins “WirelessDiagnostics.” It contains many files that describe your wireless environment in detail. A network specialist can examine them for further analysis.
Use other diagnostics utilities
Wireless Diagnostics includes additional utilities for network specialists. Open them from the Window menu in the Wireless Diagnostics menu bar:
- Info gathers key details about your current network connections.
- Logs enables background logging for Wi-Fi and other system components. The result is saved to a .log file in the diagnostics report location on your Mac. Logging continues even when you quit the app or restart your Mac, so remember to disable logging when you're done.
- Scan finds Wi-Fi routers in your environment and gathers key details about them.
- Performance uses live graphs to show the performance of your Wi-Fi connection:
- Rate shows the transmit rate over time in megabits per second.
- Quality shows the signal-to-noise ratio over time. When the quality is too low, your device disconnects from the Wi-Fi router. Factors that affect quality include the distance between your device and the router, and objects such as walls that impede the signal from your router. Learn more.
- Signal shows both signal (RSSI) and noise measurements over time. You want RSSI to be high and noise to be low, so the bigger the gap between RSSI and noise, the better.
- Sniffer captures traffic on your Wi-Fi connection, which can be useful when diagnosing a reproducible issue. Select a channel and width, then click Start to begin capturing traffic on that channel. When you click Stop, a .wcap file is saved to the diagnostics report location on your Mac.
Learn more
Additional recommendations for best Wi-Fi performance:
- Keep your router up to date. For AirPort Time Capsule, AirPort Extreme, or AirPort Express Base Station, check for the latest firmware using AirPort Utility. For non-Apple routers, check the manufacturer's website.
- Set up your router using Apple's recommended settings, and make sure that all Wi–Fi routers on the same network use similar settings. If you're using a dual-band Wi-Fi router, make sure that both bands use the same network name.
- Learn about potential sources of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth interference.
Learn about other ways to connect to the Internet.
If your wireless network isn’t working properly with your NOOK Tablet, it may be a problem with the WiFi or it may be a problem with the NOOK Tablet’s connection to the WiFi signal.
If the WiFi belongs to you, here are some ways to determine if it is the WiFi service itself:
Is the WiFi router powered up and connected to the Internet?
Does a laptop or desktop computer “see” and communicate with the adapter?
Is the Internet service working? Check this from the computer.
Use your computer’s troubleshooting tools to check its configuration. Plus, each wireless device has a built-in configuration and setup screen you can access from your computer. Here are some possible solutions:
Locate and click on the padlock icon at the bottom right of the window, and you need to enter your admin password.Step 4. Right-click on iTunes and select Get Info.Step 3. 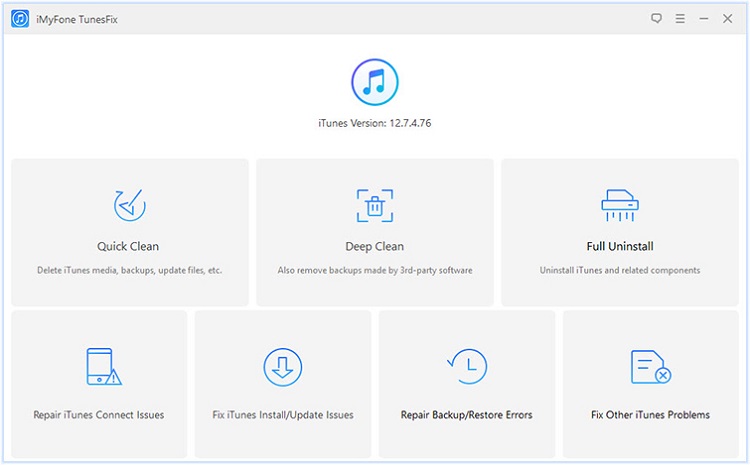
Turn off your NOOK Tablet and then turn it back on.
Turn off the power to the router for ten seconds or so and then restore power. That may fix a problem that has cropped up in the internal memory of the router.
Check with the network administrator to see if there’s a blacklist (of blocked devices) or a whitelist (of devices that are specifically allowed entrance) for the system if you’re trying to connect to a secured system (at an office or somewhere similar).
You may need to provide your NOOK Tablet’s MAC address (its unique identifier). To find your NOOK Tablet’s MAC address, go to Settings, tap Device Info, and tap About Your NOOK. There is your MAC address.
If all else fails, call Customer Service at 1-800-843-2665.
I see a wireless network but can’t get a good connection
WiFi networks cover a relatively small area (about the size of a small house). It may take a bit of experimentation to determine the actual working area for the WiFi system you want to use.
Tap the network to which you want to connect, and then tap the Forget command. This erases previous settings for the connection. Then tap the same WiFi network name and see if the second time is the charm.
Go to Settings. In the Wireless section, look at the names of networks that the NOOK Tablet has discovered. Signal strength is shown to the right of each name: one to four stacked curves. Four curves means a strong signal. One curve means a weak signal, which may fade in and out.
Take your tablet close to the WiFi router or transmitter (7 feet away). Make sure no major pieces of metal are around to block the signal: refrigerators, file cabinets, or steel desks. (In some places, signals can be blocked by steel mesh in the walls.)
I see the network but I can’t connect to it
Most wireless networks use a security system to keep unwanted outsiders from using them. You usually need a key or password, and some also require a username. You have to enter the key exactly. If the key is 6sJ7yEllowbIRD, then that is how you must enter it.
Mac Connected But No Internet
If your wireless system is at your home or office and you can’t make it work with all of your devices, it might make sense to reset the WiFi router to its factory default settings and reconfigure it with all of your devices ready to be connected. Consult the instruction manual for the WiFi system to learn how to do this.
Imac Connected To Wifi But No Internet
The NOOK Tablet doesn’t currently support voice-over-Internet services like Skype or Comwave, and Barnes & Noble has indicated it probably won’t go there; it wants to concentrate on things related to reading and writing.